
🌏 Hot off the press: China’s 15th plan for the era of security
A breakdown of China’s new FYP and what it means for the next decade of the energy transition
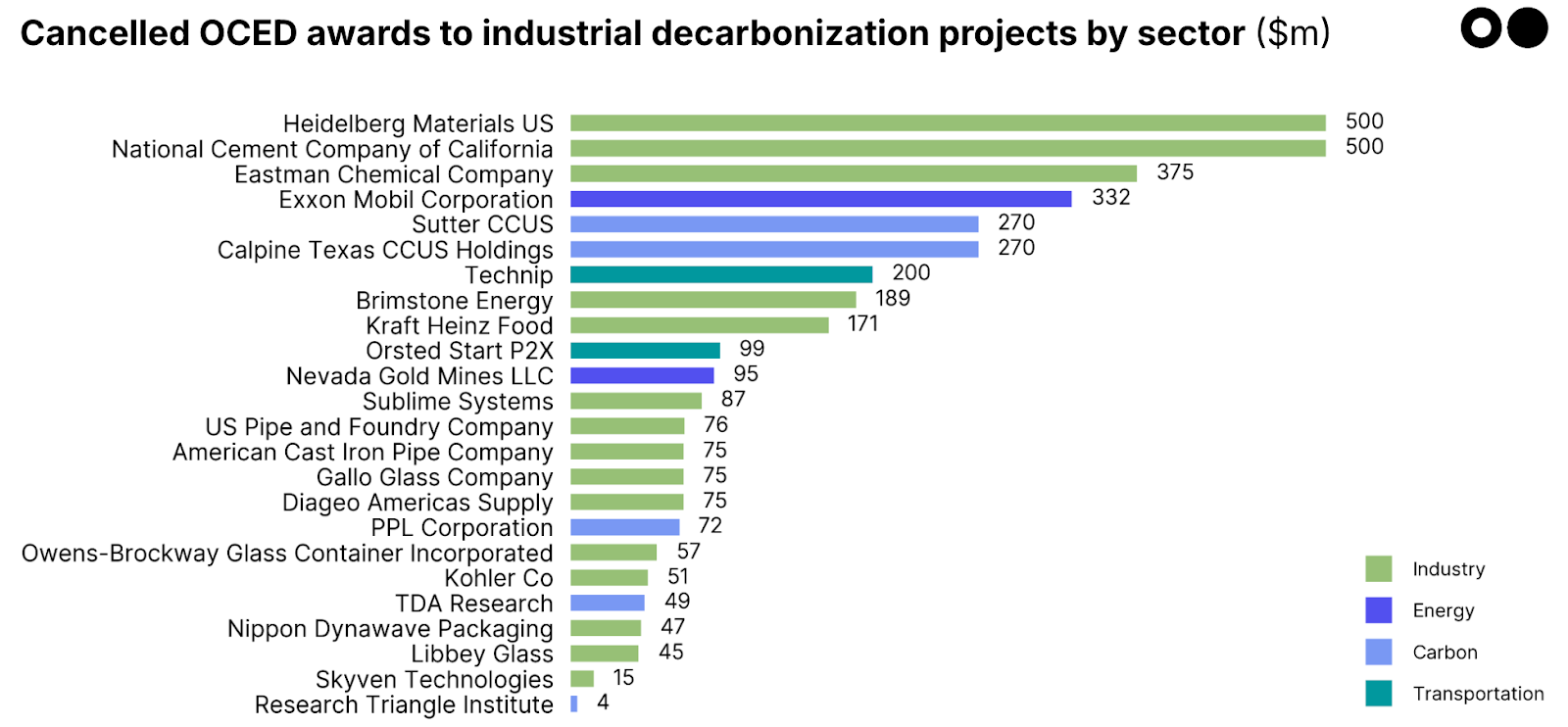
Federal funds canceled for clean cement, steel, heat, CCS projects
Happy Monday!
The DOE just pulled $3.7bn from 24 major clean energy projects — a reversal that threatens the US' industrial decarbonization. Here’s what got cut, and why it matters.
In deals, $284m for sustainable aviation fuels, $270 for nuclear across two deals, and $38m for electronics manufacturing.
In other news, Sophie’s newly closed climate venture fund, US state clean energy news whiplash, and new planetary temperature projections.
Thanks for reading!
Not a subscriber yet?
📩 Submit deals and announcements for the newsletter at [email protected].
💼 Find or share roles on our job board here.
Last Friday, in a late-afternoon news dump, the Department of Energy announced it is canceling $3.7bn in funding across 24 clean energy projects. It’s the most sweeping climate funding rollback yet under the Trump administration — and a direct hit to the Office of Clean Energy Demonstrations (OCED), the federal office created to commercialize first-of-a-kind (FOAK) decarbonization technologies.
Led by newly appointed DOE Secretary Chris Wright, the department recently launched a sweeping review of $15bn in awards across 179 projects. Now the results are in: 24 OCED projects have been terminated, cutting across nearly every corner of industrial decarbonization — low-carbon cement, carbon capture, hydrogen, clean fuels, electrified heat, and materials like glass and steel.
Wright framed the cancellations as a cost-saving measure, claiming the projects “failed to advance the energy needs of the American people” and wouldn’t deliver “a positive return on investment.” Nearly 70% of the canceled awards, he said, were issued during the final weeks of the Biden administration.
But these weren’t fringe initiatives. OCED, launched in 2021 and backed by more than $25bn from the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law and Inflation Reduction Act, was designed to bridge the commercialization gap, supporting diligenced projects with proven technologies and unproven markets. The office offered non-dilutive, cost-share awards (up to 50% of capex), with funds released in tranches tied to development milestones. Many of the projects had not yet drawn down their full awards.
Among the hardest-hit sectors:
Sightline clients can explore clean industrial project deployment charts on our platform here. If you’re interested in becoming a client, speak with us here.
OCED was one of the most ambitious tools the federal government had for scaling climate infrastructure. Its model was to de-risk market adoption, not technology development — helping FOAK projects attract follow-on capital and reach liftoff. Many canceled projects had signed offtake agreements, EPC contracts, and local partnerships in place. Several were already breaking ground, and notably, many were located in red-state manufacturing hubs, promising to deliver jobs and economic benefits to disadvantaged communities.
Cement has been hit hardest: including projects not finalized, the total public support now pulled from the sector stands at $1.5bn (including not-awarded funds), or 94% of federal funds earmarked for low-carbon cement under the Industrial Demonstrations Program. These projects represented nearly 60% of planned low-carbon cement capacity in the US.
This is a major setback for industrial decarbonization, at a time when the Trump administration says it wants to strengthen US manufacturing competitiveness (👀 tariffs). Sectors like cement, CCS, hydrogen, and clean heat, all facing offtake and cost hurdles, just saw their commercialization timelines stretched — or erased entirely.
Additionally, according to the Center for Climate and Energy Solutions, the cancellations could result in 25,000 lost jobs and $4.6bn in lost economic output.
⚡ SkyNRG, an Amsterdam, Netherlands-based sustainable aviation fuel producer, raised $284m in Growth funding from APG Asset Management.
⚡ Radiant Nuclear, an El Segundo, CA-based micro nuclear reactor developer, raised $165m in Series C funding from DCVC, Crossbeam Venture Partners, Giant Ventures, Gigascale Capital, and other investors.
🥩 Volare, a Helsinki, Finland-based insect-based protein and oil producer, raised $29m in Growth funding from Finnish Climate Fund, Finnvera, Firstminute Capital, Maki.vc, Norion Bank, and Springvest.
⚡ Battery Smart, a Gurgaon, India-based battery swapping network service, raised $29m in Series B funding from Rising Tide Energy, Ecosystem Integrity Fund, LeapFrog Investments, and responsAbility Investments.
🏭 ecop, a Vienna, Austria-based high-tech heat pump manufacturer, raised $12m in Growth funding from European Innovation Council, KSB, EIT InnoEnergy, Finadvice AG, and New Energy Technology (AUS).
⚡ Heron Power, a Santa Cruz, CA-based power electronics manufacturer, raised $38m in Series A funding from Capricorn Investment Group, Breakthrough Energy Ventures, Energy Impact Partners, Gigascale Capital, Powerhouse Ventures, and other investors.
🏠 Gridcare, a Redwood City, CA-based grid investment optimization platform, raised $14m in Seed funding from Xora Innovation, Acclimate Ventures, Aina Climate AI Ventures, Breakthrough Energy Ventures, Clearvision Ventures, and other investors.
⚡ Volteras, a London, England-based EV charging software, raised $11m in Series A funding from Union Square Ventures, Edenred, Exor Ventures, Long Journey Ventures, and Wex Venture Capital.
⚡ Atomic Canyon, a San Luis Obispo, CA-based AI platform for the nuclear industry, raised $7m in Seed funding from Energy Impact Partners, Commonweal Ventures, Plug and Play Ventures, Tower Research Capital, and Wischoff Ventures.
🚗 Kite Magnetics, a Clayton, Australia-based advanced magnetic materials developer, raised $4m in Seed funding from SQM Lithium Ventures.
🏠 Sophia Space, a Seattle, WA-based orbital data center developer, raised $4m in Pre-seed funding from Unlock Venture Partners.
🌱 Calice, a Buenos Aires, Argentina-based AI-powered agricultural software platform, raised $3m in Seed funding from Air Capital, Astanor Ventures, Draper Cygnus, GrainCorp Ventures, Innventure, and Xperiment Venture.
⚡ NANO Nuclear Energy, a New York City, NY-based advanced nuclear microreactors manufacturer, raised $105m in Post-IPO Equity funding.
⚡ Plagazi, a Gothenburg, Sweden-based green hydrogen developer, raised $33m in Grant funding from EU Innovation Fund (EIF).
⚡ Viotas, a Limerick, Ireland-based smart electricity management platform, raised $11m in Debt funding from Claret Capital Partners.
♻️ Circular Brain, a Jundiaí, Brazil-based electronic waste lifecycle management platform, raised $4m in PE Expansion funding from Lorene.
🏭 Heliogen, a Pasadena, CA-based concentrated solar developer, was acquired by Zeo Energy for $10m.
🥩 MeliBio, an Oakland, CA-based microbial-based honey producer, was acquired by FoodYoung for an undisclosed amount.
Mitsubishi UFJ Capital, a Tokyo, Japan-based investment firm, launched a $190m flagship fund, MUC-10, to support long-term startup growth in Japan, particularly in deep tech.
Gresham House, a London, England-based investment firm, closed its forestry fund, Forest Fund VI, with $507m to support carbon sequestration of 4.7m tonnes of CO2 over 25 years, while also targeting biodiversity preservation and flood mitigation.
Can’t get enough deals? See full listings and deal analytics on Sightline Climate.
The global average temperature is projected to approach almost 2°C above pre-industrial levels within the next five years, nearing the critical threshold set by the Paris Agreement. This new World Meteorological Organization forecast highlights the pressing need for immediate mitigation and growing need for adaptation.
President Trump signed executive orders to quadruple US nuclear capacity to 400 GW by 2050, fast-track reactor licensing, and boost domestic uranium production to meet surging power demand from sectors like AI. The orders also relax radiation safety standards and streamline regulatory processes, sparking concerns about oversight and public safety. While the move has energized nuclear startups and uranium miners, critics warn it could erode trust and complicate long-term industry growth.
Iowa's legislature has passed a bill establishing a new state tax credit of up to $2 per gallon for sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) produced within the state. The incentive applies to SAF derived from feedstocks such as ethanol, corn oil, soybean oil, animal fats, used cooking oil, and algae, boosting the case for SAF production.
In other state policy news, three proposed anti-solar bills in Texas have failed to advance in the state House, blocking a major push to impose new restrictions on renewable energy. The measures would have introduced new fees, permitting barriers, and retroactive requirements forcing existing renewable projects to install backup power, while mandating that half of all new generation come from non-renewables. Their defeat helps preserve Texas’s leadership in solar and reflects growing bipartisan recognition of the economic and grid benefits of renewables.
Meanwhile in NY, a controversial natural gas pipeline that was canceled in 2020 is being restarted. Following talks between President Trump and Governor Kathy Hochul, this signals a shift in political support after years of legal hurdles, and is apparently part of the bargain to reopen the offshore NY wind project that Trump issued a stop-work order on. It’s a sign of how the clean energy transition hangs in the balance of political headwinds and tailwinds.
Our very own Sophie Purdom in the WSJ about Planeteer’s first venture fund close.
A clean project done ahead of schedule and under budget.
The 10-year court case against a German utility from a Peruvian farmer is over (for now).
Another court case – Trump’s tariffs are illegal (probably).
Rainbow morphocolor solar panels.
An interview with Fortsecue’s head of hydrogen as he retires and reflects.
Elon’s out at DOGE.
💡 VINE Connect Applications: Apply by June 13, 2025 to participate in a program designed for up-and-coming agricultural technology providers, from VINE Connect, to connect them to sell to farmers across California.
📅 Financing the Future: How NYC is Investing in Climate Progress: Join us on June 26th, 2025 in Manhattan for a deep dive into how financial leaders, investors, and sustainability experts are channeling funds into NYC’s climate future amid political and economic uncertainty.
📅 Cleantech Venture Day London & Climate Tech SuperCluster Forum: Get your ticket for June 25th, 2025 at KPMG Crimsonwing, 15 Canada Sq (map link), London. A full-day forum connecting climate tech startups with investors and showcasing cross-sector innovations from Europe’s leading cleantech clusters.
📅 Biodiversity Showcase: Join on June 3rd, 2025 from 1:00–3:00 PM (networking until 4:00 PM) to explore innovative technologies and solutions advancing biodiversity monitoring and restoration across the UK.
Climate Investment Fellowship (Tech background) @World Fund
Chief of Staff @Floodbase
Global Communications Manager @Carbon Business Council
Analyst @Hitachi Ventures
Research Associate @Molecule Ventures
Executive Director @Arête Glacier Initiative
📩 Feel free to send us deals, announcements, or anything else at [email protected]. Have a great week ahead!

A breakdown of China’s new FYP and what it means for the next decade of the energy transition
Beijing lowers growth targets while doubling down on AI, energy, and advanced industry
A new weekly briefing on the moves and motives shaping power markets